- Have any questions?
- +61 424 178 561
- +61 3 9837 5203
- [email protected]
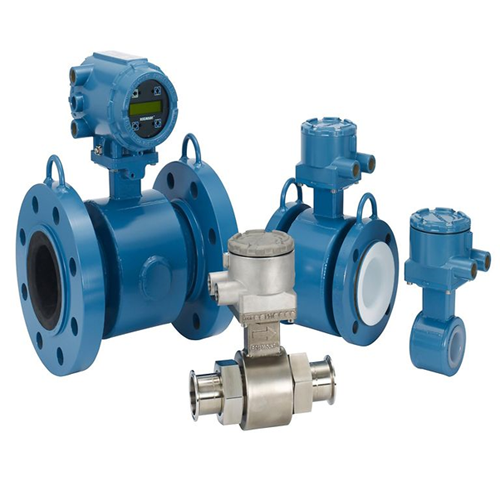
Electromagnetic Flowmeter
An Electromagnetic Flowmeter is also more commonly just called a Mag Flowmeter. Electromagnetic flow meter consists of sensors and converters in two parts. The product is based on Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, used to measure the conductance greater than 20 μS/cm volume of conductive liquid flow. In addition to the general volume of conductive liquid flow, also can be used to measure strong acid, alkali and other strong corrosive liquids & mud, pulp and liquid-solid two-phase suspension of uniform volume flow.
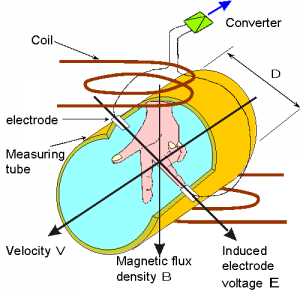
The Electromagnetic flow meter or Mag flow meter uses Faraday’s Law of electromagnetic induction to measure the process flow.
When an electrically conductive fluid flows in the pipe, an electrode voltage E is induced between a pair of electrodes placed at right angles to the direction of magnetic field. The electrode voltage E is directly proportional to the average fluid velocity V.
E=kBDV
Where,
k——–Instrument constant B——–Magnetic induction density
V——–Average velocity in the cross section of a measured pipe
D——–Inner diameter of a measured pipe
When measuring flow rate, the conductive liquid flows at a velocity of V perpendicularly through a magnetic field, which inducts a voltage that is direct proportional to the average velocity. The inducted voltage signal is measured on two or more poles immediately contacted with the liquid, sent to a convertor through the cable, and then intelligentized before it is transferred to and displayed in a LCD or converted into 4~20mA or 0~1kHz output.
Besides measuring flow of general conductive liquid, magnet meter can measure flow of liquid-solid mixed fluid, high-viscosity fluid and salt, strong acid and strong alkali to be used as chemical flow meter, sanitary flow meter or sewage flow meter.
Features:
- Size : DN3-DN3000mm (1/8”~120”)
- Medium temperature:
Integral type : -20℃~60℃
Remote type (Rubber & Polyurethane liner): -10℃~80℃
Remote type (PTFE & PFA & F46 liner): -10℃~160℃ - Integrated verification, diagnostic function and empty pipe detection
- Measure forward and reverse direction flows
- The display allows concurrent monitoring of total and instantaneous flow rates in two rows
- Built-in reference electrodes
- High protection grade available IP65 & IP68
- No moving parts, no pressure loss
- High accuracy: ±0.5% RO, (±0.3% & ±0.2%) optional, velocity >0.3 m/s




